Environmental preservation and building environmentally-friendly societies

We comply with laws and regulations related to chemical substance control and the environment, and are conducting activities to protect biodiversity.
Basic philosophy
In addition to strengthening the selection and management of chemical substances to create products and processes that are kind to people and the earth, we are improving environmental management in things such as compliance with laws, regulations and customer standards in every country where we do business, based on ISO 14001.
We are also maintaining a company woodland, creating biotopes, and working to preserve tidal flats and other areas for biodiversity.
Control and reduction of substances of concern
Control of chemical substances contained in products
To strengthen the management of chemical substances in our products, we control legally regulated substances in each country, substances that are self-regulated by automakers, and substances covered by our own company regulations. We monitor the trends in European REACH*1 regulations and the EU RoHS Directive*2 and have a system in place to respond rapidly when these regulations are revised. To respond to requests from automakers in each country for information on chemical substances in products, we have devised mechanisms and conducted systems for global collective management of chemical substances that we are currently using in Japan, China, Thailand and Vietnam. We will be steadily expanding this system to places where it is not yet in use.
- *1 Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals
- *2 Restrictions on the use of specific hazardous substances contained in electrical and electronic equipment
■Chemical substance regulations in each region
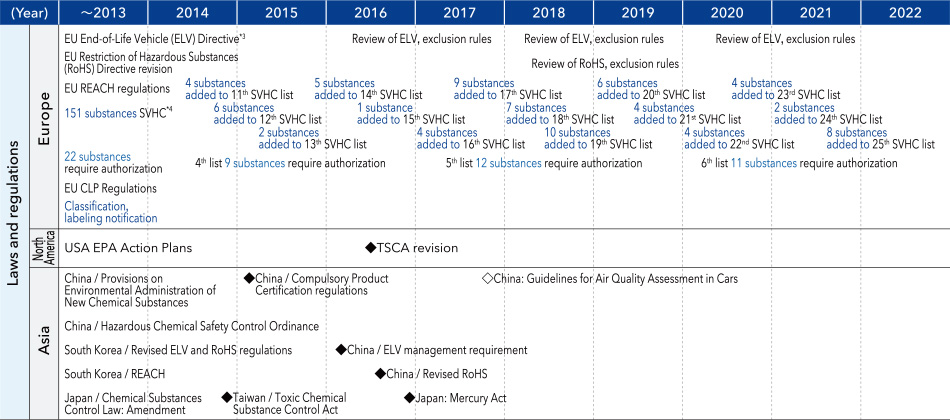
- *3 Restrictions on the use of substances of concern contained in automobile parts and materials
- *4 Substances of high concern
Reduced use of substances of concern
In production processes, we are switching to water-based paint and release agents, making painting lines more compact, improving coating efficiency, and making other efforts to reduce Pollutant Release and Transfer Register (PRTR) substances and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Through on-site visits, we also share information on cases in which VOCs were successfully decreased to promote reduction activities.
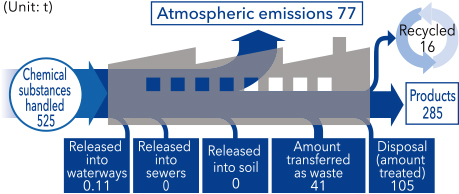
■Volumes and flow of emitted PRTR substances
■VOC emissions, emissions per sales unit (index)*5
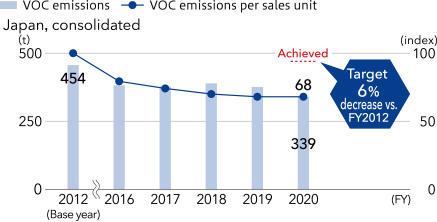
- *5 Emissions per sales unit (index) is a figure obtained taking FY2012 as 100
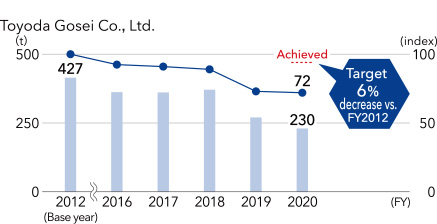
- *5 Emissions per sales unit (index) is a figure obtained taking FY2012 as 100
Activities for living with nature that build ties with the community
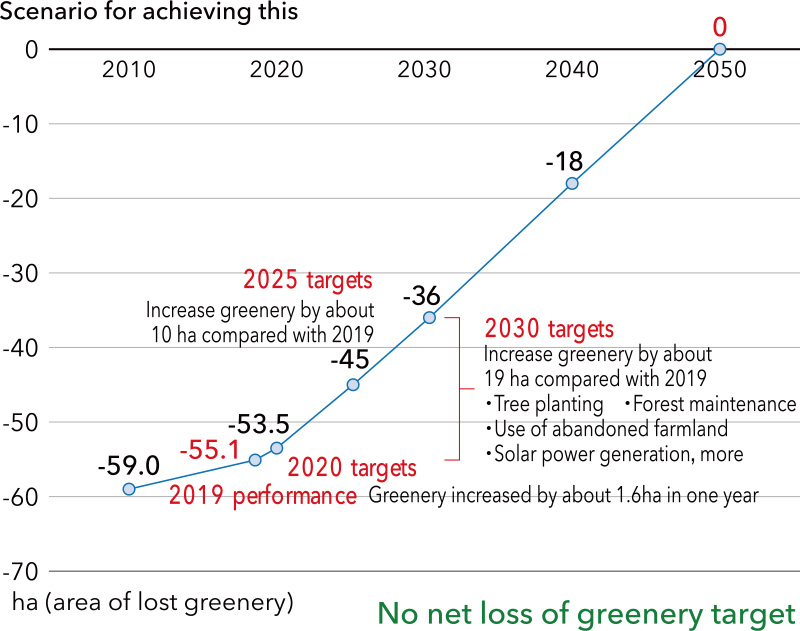
The Toyoda Gosei Group has set a target of no net loss of greenery; that is, restoration of greenery equivalent to the area of its plants, by 2050. To achieve that, we are maintaining mountain woodlands, removing invasive species from rivers, installing biotopes, and protecting tidal flats by the ocean.
In conjunction with the Toyota Group, government agencies, NPOs and other organizations, we are also enhancing our activities for nature-friendly living.
Long-term targets for 2050
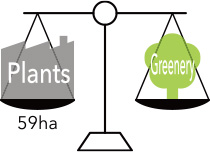
The area of Toyoda Gosei plants is 59 hectares, and despite environmental considerations some nature was destroyed in their construction. We have set a target and are now working toward “No net loss of greenery,” in which we aim to restore greenery to an area that is the same size as that of our plants by 2050.
■Achieving no net loss of Greenery
Restoring the greenery lost in plant construction in an activity to live with nature
■Activities to achieve no net loss of greenery
■Working to save our water, the source of life on earth
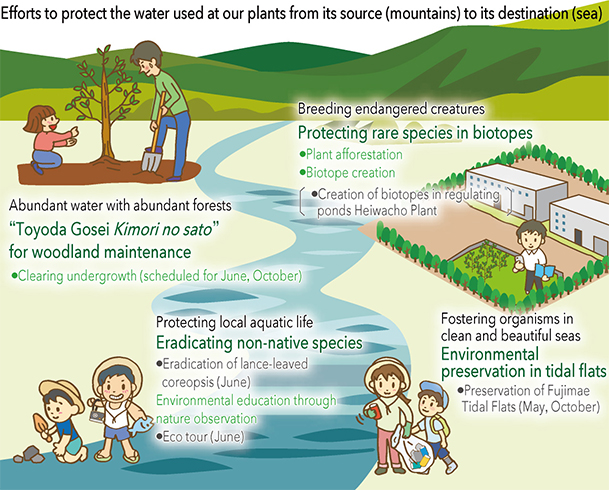
Kimori no sato woodland maintenance
In FY2019 we cleared undergrowth and thinned trees in a forest in Minokamo, Gifu Prefecture, located on the upper reaches of the Kiso River to promote healthy woodlands.

Biotope creation
We conducted a biological survey of the biotope completed in FY2018 at the Heiwacho Plant. Five themes and five species that are Aichi Prefecture Ecosystem Monitoring Indicator Species were confirmed, and living organisms have begun to gradually become established.

Creation of biotope*6 in plant regulating pond
A biotope was completed in November 2018 using a rainwater regulating pond*7 at Toyoda Gosei’s Heiwacho Plant (Aichi Prefecture, Japan). Creating a biotope with a regulating pond is unusual in Japan, and this was the first such effort in Aichi Prefecture.
This biotope was developed as an environment to foster rare organisms threatened with extinction. In addition to serving as a gene bank for Nagoya Dharma pond frogs and Japanese medaka fish, seeds of plants such as the Tokai dandelion are provided to other organizations. We also plan to use it as a learning site for local schoolchildren.
These activities are carried out in coordination with the All Toyota Green Wave Project and the Owari Seibu Ecosystem Network.*8
- *6 Derived from the Greek bios (life) and topos (place). An environment that provides a habitat for a distinct assemblage of organisms.
- *7 Ponds established in residential areas or industrial plants, which function to temporarily store rainwater during local severe rainstorms and prevent flooding.
- *8 One of nine such councils in Aichi Prefecture, established in November 2016. It consists of 45 groups, including NPOs and schools in the western Owari region, and serves as an ecosystem network.

-
 Japanese dandelion
Japanese dandelion
-
 Japanese medaka
Japanese medaka
-
 Nagoya Dharma
Nagoya Dharma
pond frog
Participation in cleanup activities for the Fujimae Tidal Flat
In October 2018, employees and their families picked up large volumes of polystyrene foam, plastic bottles and other trash that had accumulated on the banks of the Fujimae Tidal Flat to protect its ecosystem. The Fujimae Tidal Flat is located in Nagoya and registered in the Ramsar Convention.*9 This provided an opportunity for participants to think about the environment, including understanding that birds and fish sometimes die from eating such trash and observing the animals (crabs, mudskippers, clams) that live in the tidal flat, which is not normally open to the public. This cleanup activity is held every year in cooperation with local residents and an NPO.
- *9 An international treaty on the preservation and regeneration of wetlands that are waterfowl habitats. It was adopted in Ramsar, Iran in 1971.
Participation in the eradication of Lance-leaved Coreopsis*10
In June 2018, we participated in an activity to get rid of Lance-leaved Coreopsis, an invasive plant species, that was held in the city of Miyoshi in Aichi Prefecture. About one ton of the plant was removed. This was done at the request of the prefectural government with the aim of protecting native plant species. The All Toyota Green Wave Project participated in cooperation local residents.
- *10 This flower was imported into Japan from overseas as an ornamental plant, but it propagates strongly and crowds out native species. It was recently classified as a designated invasive species, and its cultivation and sale are prohibited.

Ecosystem preservation activities in Lake Izunuma-Uchinuma, Miyagi Prefecture
In October 2018, employees of TG East Japan Co., Ltd. and their families conducted ecosystem protection activities, such as cutting excessive reeds growing in Izunuma and Uchinuma in northern Miyagi Prefecture.
Izunuma and Uchinuma are registered in the Ramsar Convention*9 because they are inhabited by more than 30 species of water birds, and they are wintering places for migratory birds including swans, white-fronted geese, and mallards. We work with the local environmental protection foundation*11 every year to help protect the ecosystem.
- *11 The Miyagi Prefectural Izunuma-Uchinuma Environmental Foundation
-
 Maintaining a walking path
Maintaining a walking path
-
 Cutting down reeds
Cutting down reeds
Mapping living creatures near our plants
In FY2020, we conducted surveys of living creatures near our plants in Japan and created biology maps. With the aim of living together with nature, we are now using these maps for the protection of ecosystems, including activities to eliminate invasive species and protect rare species.
We are also educating employees on these issues.
Activities to eliminate compliance and environmental violations and complaints
Regular checks are conducted by expert departments and maintenance and management are carried out to ensure legal compliance and no environmental problems or complaints. Preventive activities such as environmental preservation project team activities are also conducted to combat risks. In addition, we analyze problems that occur at other companies, inspect similar facilities including those at domestic and international affiliates, and take preventive measures. There were no occurrences of environmental abnormalities in FY2020.
Proper disposal and storage of PCB-containing equipment
The law stipulates that hazardous and persistent PCB (polychlorinated biphenyl) waste must be disposed of by the end of March 2027. We started outsourcing this disposal in FY2006 for the proper treatment of equipment that contains PCBs. By FY2020, 896 units had been treated.
We will continue to process untreated low-concentration PCB waste at an early stage. Until that is completed, appropriate management based on the PCB Special Measures Law is done to prevent runoff and soil contamination.
| Category | Type | No. of units treated | Treated weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| High concentration PCB waste material (PCB levels: >5,000 mg/kg) |
Ballast, power capacitors, etc. | 802 units | 6.9t |
| Low concentration PCB waste material (PCB levels: 0.5–5,000 mg/kg) |
Transformers, power capacitors, etc. | 94 units | 80.3t |
-
 Treatment of PCB waste
Treatment of PCB waste
Protecting soil and groundwater
We carefully monitor and treat soil and groundwater contamination from toxic subs tances such as trichloroethylene, which was formerly used in cleaning agents. We have established observation wells at each plant, and regularly confirm that there is no soil or groundwater pollution from toxic substances and oils.
| Location | Target | Status of corrective measures |
|---|---|---|
| Haruhi Plant | Groundwater | Purification in progress (proactive treatment, as contamination from off-site sources is possible) |
| Inazawa Plant | Groundwater | Because substances we have no history of using have been detected, regular reports to the government contain results of measurements only *Results below reference values since 2010 (government reports concluded in FY2012) |
Mottainai check
To eliminate waste of resources, we have performed plant inspections and regular mottainai inspections for corrective treatment since 2018.
Since 2021, production engineering departments have also been involved in the inspections, and executives in charge of the environment and leaders of each plant perform the inspections with a focus on places where remnants and waste materials generated in production processes are kept. The thoroughness of sorting and kaizen for recycling are investigated.
-
 Mottainai inspection / Inazawa Plant
Mottainai inspection / Inazawa Plant
- Contributing to Environmental Preservation Through All Our Business Activities
- Environmental Action Plan
- Building a Decarbonized Society
- Building a Recycling Society
- Environmental Preservation and Building Environmentally-Friendly Societies
- Environmental Management
- Collaboration with External Organizations
- Environmental Efforts at Affiliated Companies
- Environmental Data
- Third-Party Verification
- TCFD
- Third-Party Assessment

